Challenges of Human Resource Management in the 21st Century

In the Evolving 21st Century, Like other Departments of a business or organization, HRM is also rapidly evolving, with new trends and acquisitions hitting it hard. So, Challenges of Human Resource Management in the 21st Century and the HR management team to stay aligned with the best practices.
In this comprehensive guide, we will discuss some of the challenges like:
- Significant HRM Challenges
- Acquisition of Talent Skill
- Employee Engagement
- Adaptability
- Solutions to the Challenges
- And many more.
So, let’s Begin the journey and redirect the links to the bumps and hurdles of Human Resource Management.
Key Takeaway
- HRM is a Bridge between Administration and Employees
- HR focuses more on Quality Hiring as compared to other HR Features
- As technology advances, it is challenging for HR to compete in the market.
- Globalization requires more attention as it is multifaceted
- Employee well-being is now a more concern issue after the COVID-19 pandemic
Table of Contents
Introduction to Human Resource Management (HRM)
Before diving deep into the challenges of HRM in the 21st century, we introduce the concept. HRM is the strategic approach to managing an organization’s human resources.
HRM is the strategy element for managing the human resources of an organization. It fences various functions, including recruitment, talent management, employee relations and development, performance evaluation, and training.
The primary responsibility of HRM is to ensure that an organization has the right people in the right roles to achieve its objectives.
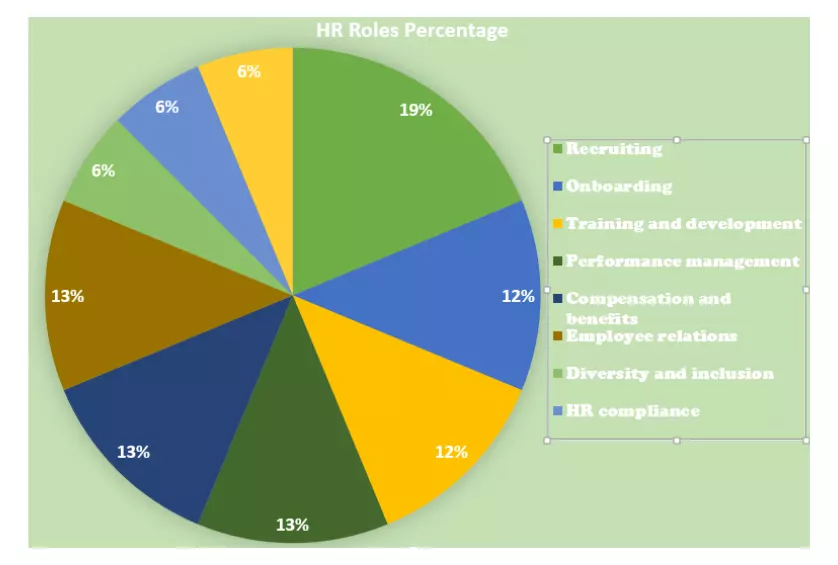
Percentage of HR Skills:
Challenges of Human Resource Management in the 21st Century: Understanding 9 Significance of Key Challenges
While Human Resource Management (HRM) undoubtedly plays a pivotal role in the Present-era business environment, it also faces many challenges. These challenges:
1. Acquisition of Talent and Management Skills: The Competitive Challenge
In the 21st Century, it is a massive challenge for HRM to acquire and retain top talent. Competition in today’s market is too high.
HRM must continuously transform and adapt its strategies to ascertain, attract, and retain the best talent in the industry. The challenge lies not only in staffing but also in crafting compelling employer brands and employee value propositions.
The war for talent means organizations must stand out as attractive employers.
Low retention rates may be expensive and annoying.
Offering competitive benefits packages can be an essential retention tool.
Presenting chances for professional advancement.
2. Employee Engagement and Productivity: The Engagement Challenge
HRM practices directly influence employee engagement and productivity, essential drivers of an organization’s achievement. However, engaging employees in a significant way can be a challenge.
To effectively motivate and inspire its diverse workforce, the organization must adeptly communicate its mission and values. The difficulty is fostering interest at work and utilizing each employee’s distinct abilities.
3. Compliance and Legal Requirements: The Regulatory Challenge
Staying submissive to labor laws and regulations is imperative in a progressively regulated world.
HRM serves as the frontline against potential legal risks and liabilities. This challenge includes understanding and observing complex labor laws and implementing policies and practices that promote diversity, equity, belonging, and inclusion (DEBI) while preventing workplace discrimination and harassment.
The challenge here is the thorough consideration of detail and the constant monitoring needed to ensure compliance.
4. Adaptability: The Skills Challenge
Business environments evolve rapidly, determined by technological advancements and market changes.
HRM ensures the workforce remains adjustable and equipped with the necessary skills and proficiencies. This challenge involves identifying skill gaps, providing relevant training and development opportunities, and promoting a refined culture of continuous learning.
The challenge lies in keeping the workforce current in an era where skills can quickly become obsolete.
5. Evolving Nature of HRM: The Trend Challenge
HRM Degree has evolved significantly, adapting to the changing needs of organizations and the workforce.
In the 21st Century, two significant shifts stand out: the integration of technology and the move from traditional HRM to strategic HRM.
Technology has revolutionized HRM practices. Human Resource Information Systems (HRIS) and Artificial Intelligence (AI) tools streamline HR processes, from recruitment to performance management.
However, implementing and adapting to these technologies poses challenges that HR professionals must address.
Traditional HRM focuses on administrative tasks, while strategic HRM aligns HR practices with an organization’s strategic goals. HR professionals now play a more strategic role in helping organizations achieve long-term success.
6. Impact of Technology on Human Resource Management
Technology, AI, and automation have transformed Human Resource Management in numerous ways. These advancements have led to increased efficiency but also raised challenges.
Managing sensitive employee data in an age of cybersecurity threats is a significant concern.
Ensuring employees and HR professionals proficiently using new HRM technology can be challenging. Balancing the use of technology with employee privacy rights is essential.
Automation can streamline routine HR tasks, such as payroll processing and benefits administration. However, it can also depersonalize the employee experience. HR professionals must balance automation and maintaining a human
7. Managing a diverse workforce

The modern workplace is increasingly diverse, and HRM must adapt to manage this diversity effectively.
A company’s success depends on diversity and inclusion, which are more than trendy terms.
Diverse teams bring varied perspectives, which can lead to innovation and better decision-making.
HR must actively address bias and discrimination to create an inclusive environment.
Understanding and respecting diverse cultural norms and values is essential.
Implementing inclusive hiring practices to attract a diverse talent pool. Providing diversity training to employees and leadership to promote inclusivity.
8. Globalization: Multilingual Challenges
Globalization has stretched the scope of HRM as organizations progressively operate globally. HR must navigate cultural nuances to ensure effective communication and collaboration. Providing training to employees working in different cultural contexts.
And keep in mind legal complexities complying with labor laws and regulations across multiple countries can be complex. Tailoring HR practices to suit the specific needs of each region or country.
9. Employee Well-being
The well-being and mental health of employees are gaining increasing attention. Remove the negative perception connected to mental health problems.
Mental Health has a direct impact on the retention and engagement of employees. Especially after the pandemic, it has become a big concern for the HRM to remove this stigma and provide a better work experience to the workforce.
150+ ![]()
Qualified Tutors
18 Strategies to Overcome HRM Challenges in the 21st Century:
1. Technology and Automation: Top 29 HR Software
Automation and technology are vital for HR, making work easier and hassle-free. HR software solutions like Workday, Oracle HCM Cloud, SAP Success Factors, and many others have revolutionized HR departments’ operations.
These tools can restructure everything from recruitment to payroll management, allowing HR professionals to focus on strategic initiatives rather than administrative tasks.
However, adopting such technology requires a workforce that is proficient in using it. HR professionals must invest in training and upskilling programs to ensure their teams can harness the full potential of these tools.
Following are some of the most commonly used Software for HRM:
Workday: Workday Enterprise Management Cloud gives organizations of all sizes the power to adapt through finance, HR, planning, spend management, and analytics applications. It is known for its user-friendly interface and offers many features, including HR analytics and workforce planning.
Oracle HCM Cloud: Oracle’s Human Capital Management Cloud is a comprehensive solution for managing HR processes. It offers tools for recruitment, talent management, and payroll, all integrated into a single platform.
SAP SuccessFactors: SAP’s SuccessFactors is a cloud-based HR management system that covers everything from recruitment to performance management. It is HR software that delivers experiences that help HRM achieve their goals.
ADP Workforce Now: ADP Workforce Now is a popular HR software solution offering payroll processing, tracking time and attendance, and benefits administration. ADP Workforce Now is a cloud-based platform for handling payroll, time and attendance, talent management, benefits administration, and other HR processes.
BambooHR: BambooHR is designed for small and medium-sized businesses. It helps in core HR functions, such as employee data management, onboarding, and performance management.
Zenefits: Zenefits offers a comprehensive HR platform that includes payroll, benefits, and compliance management. It is helpful for startups and small businesses.
Gusto: Gusto is known for its simplicity and ease of use. It provides payroll, benefits, and HR tools for small businesses, emphasizing employee self-service.
Paylocity: Paylocity is a cloud-based HR and payroll software known for its robust reporting capabilities and employee engagement features.
Kronos Workforce Ready: Kronos Workforce Ready offers workforce management solutions, including time and attendance, scheduling, and payroll. It’s suitable for businesses of all sizes.
Ultimate Software (UltiPro): UltiPro is a cloud-based HR and payroll solution focusing on employee experience. It includes features for talent management, onboarding, and HR analytics.
Namely: Namely is an all-in-one HR platform that covers payroll, benefits administration, and talent management. It’s designed for mid-sized companies.
TriNet: TriNet provides HR outsourcing services, including payroll, benefits, and compliance. It’s particularly suited for small to mid-sized businesses.
Paychex Flex: Paychex Flex is a cloud-based HR and payroll solution offering various services, from payroll processing to time and attendance tracking.
PeopleSoft: PeopleSoft, by Oracle, is a comprehensive HR software suite that covers HR, payroll, and talent management. It’s known for its suppleness and scalability.
HRMS (Human Resource Management System): HRMS is a generic term encompassing various software solutions to streamline HR processes. This Interface Provides better options to fit the organization’s needs.
CakeHR: CakeHR is an HR software solution focusing on ease of use and automation. It offers features for leave management, performance tracking, and employee self-service.
Bullhorn: Bullhorn is primarily known for its applicant tracking system (ATS) and customer relationship management (CRM) solutions. It’s tailored for recruiting and staffing agencies.
Glint: Glint, now a part of LinkedIn, specializes in employee engagement and performance management. It provides insights through surveys and analytics to improve the workplace experience.
Talentsoft: Talentsoft is a talent management software that covers recruiting, performance management, and learning and development. It’s designed for European markets.
Freshteam: Freshteam is a straightforward and user-friendly HR software solution. It offers tools for recruitment, onboarding, and employee data management.
Greenhouse: Greenhouse is an applicant tracking system (ATS) known for its customization options and integration capabilities. It provides better help to organizations in the Hiring process.
Jobvite: Jobvite is an end-to-end recruiting platform that covers everything from sourcing candidates to onboarding. It helps in hiring top talents.
JazzHR: JazzHR is an applicant tracking system (ATS) for small and mid-sized businesses. It offers features for job posting, applicant tracking, and interview scheduling.
Recruitee: Recruitee is a collaborative hiring platform that allows teams to work together on recruitment. It includes features for sourcing candidates, tracking applicants, and managing interviews.
Lever: Lever is an applicant tracking system (ATS) that focuses on improving collaboration among hiring teams. It offers features for sourcing, interviewing, and candidate engagement.
WorkBright: WorkBright is an onboarding software designed to streamline the new hire process. It includes features for digital document collection and compliance management.
Breezy HR: Breezy HR is an applicant tracking system (ATS) that offers sourcing, interviewing, and hiring tools. It’s known for its user-friendly interface and customizable workflows.
HR Cloud: HR Cloud provides software solutions for onboarding, document management, and employee engagement. It’s designed to simplify HR processes.
Factorial: The HR software platform covers HR management, time tracking, and employee benefits. It’s designed for small and medium-sized businesses.
Each of these HR software solutions brings unique features and advantages. So you have to choose your Management tool as per your requirements.
2. Creating an Inclusive Workplace
HR must keenly work to create a comprehensive environment where employees from varied backgrounds feel appreciated and heard. It includes applying strategies such as diverse hiring practices and inclusive management training.
Organizations like Google, Microsoft, and Salesforce have made significant paces in embracing diversity and inclusion.
They are excellent examples of how a commitment to these principles can positively impact company culture and the bottom line.
3. Managing the Global Workforce
As companies expand their reach globally, HRM must adapt to manage a diverse and dispersed workforce. Cross-cultural training becomes crucial in this context, enabling employees to collaborate effectively across borders and time zones.
Globalization also brings with it legal and compliance challenges. HR professionals must stay informed about labor laws and regulations in multiple influences.
Implementing a solid compliance management system is essential to avoid costly legal matters.
4. Attracting and Retention of Top Talent
Top talent is also a critical factor in the progress of an organization. Employer branding, highlighting company culture, and offering growth opportunities are just ways HR professionals can convince potential candidates.
Once talent is acquired, retaining it is equally important. HR should focus on employee engagement strategies, including mentoring programs, recognition initiatives, and continuous feedback loops. Competitive compensation and benefits packages also play a significant role in employee retention.
5. Promoting Employee Well-being
The well-being of employees has turned into a central concern in HRM. Mental health programs, stress management workshops, and flexible work arrangements are essential for promoting employee well-being. A happy and healthy workforce is more productive and loyal.
Companies like Google, known for their innovative approach to employee well-being, have set the standard for the industry. They showcase the positive impact of prioritizing employee health and happiness.
During times of crisis, employee well-being becomes paramount. HR should implement support systems, such as mental health resources and flexible work arrangements, to help employees cope with uncertainty and stress.
These practices were well observed during the COVID-19 pandemic when every renowned organization created a better plan for the well-being of their employees.
6. Ensuring Legal Compliance
Staying compliant with labor laws and regulations is non-negotiable for HR professionals. They must comprehensively understand relevant laws and regularly update policies to ensure adherence.
Case studies of companies that faced legal challenges can provide valuable insights. Understanding how these companies resolve issues can help HR professionals avoid similar pitfalls.
7. Filling the Skills Gap
HR professionals should continuously assess their organization’s skill gaps. It requires open communication with department heads and a proactive approach to identifying improvement areas.
8. Employee Data Privacy and Security
In an era where data breaches and cyber threats are prevalent, HR professionals must prioritize the security and privacy of employee data. Implementing robust cybersecurity measures and strict data access controls is essential to safeguard sensitive information.
Suppose the HR Department neglects data protection regulations. In that case, this non-compliance can result in severe fines and damage to an organization’s reputation.
They must stay informed about data protection regulations like GDPR and CCPA. Regularly audit data handling practices to ensure adherence to these regulations.
9. Leveraging Analytics for Informed Decision-Making
HR professionals can no longer rely solely on intuition when making decisions. The use of HR analytics tools can provide valuable insights into workforce trends, employee performance, and areas in need of improvement.
These insights empower HR to make data-driven decisions that benefit the organization.
Predictive analytics furthers HR, allowing professionals to anticipate future workforce needs and challenges. By identifying potential issues in advance, HR can develop proactive strategies to mitigate them.
10. Remote Work and Hybrid Workforces
The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the shift toward remote work, making it a significant HR challenge. HR professionals must adapt policies and practices to support remote employees effectively.
This includes providing the necessary technology, setting clear expectations, and addressing the challenges of remote collaboration.
As organizations transition to a post-pandemic world, many are adopting hybrid work models. HR must balance in-office and remote work, ensuring fairness and productivity. Strategies for managing hybrid workforces include flexible scheduling and clear communication channels.
11. Corporate Responsibilities and Initiatives
Organizations are increasingly expected to demonstrate commitment to environmental, social, and governance (ESG) initiatives. HR plays a vital role in these efforts by promoting ethical practices, sustainability, and social responsibility within the company.
Many job seekers today are drawn to organizations that align with their values. HR can attract purpose-driven talent by showcasing the company’s commitment to ESG initiatives in recruitment efforts.
13. Agility in HR
The modern business landscape is characterized by rapid change. Agile HR is an approach that allows HR departments to respond quickly and flexibly to changing circumstances. It involves adapting to new technologies, organizational structures, and market dynamics.
Agile HR also emphasizes continuous improvement. HR professionals should regularly review and adjust their strategies to align with the organization’s evolving goals and challenges.
14. Employee Feedback and Surveys
Employee feedback is invaluable for HR professionals. Regular surveys and feedback mechanisms allow HR to understand employee concerns, gauge satisfaction levels, and make improvements accordingly.
More is needed to collect feedback; HR must also take action. Addressing employee concerns demonstrates a commitment to their well-being and fosters a culture of trust and open communication.
15. Building a Culture of Continuous Learning
In the rapidly evolving landscape of the 21st century, knowledge becomes outdated quickly. HR professionals should encourage a culture of continuous learning within their organizations. This not only helps employees stay relevant but also fosters innovation and adaptability.
Invest in learning platforms and resources that empower employees to upskill and acquire new knowledge. This can include online courses, workshops, and mentorship programs. By providing growth opportunities, HR supports both individual and organizational development.
150+ ![]()
Qualified Tutors
16. Agile Recruitment Strategies
Talent needs can fluctuate rapidly, requiring HR to adopt agile recruitment strategies. This might involve building talent pipelines, using data-driven hiring practices, and being open to unconventional talent sources.
The gig economy has become a significant part of the modern workforce. HR can tap into this talent pool for specific projects or roles, providing flexibility for the organization and workers.
17. Employee Experience Enhancement
Employee experience is a crucial factor in talent attraction and retention. HR professionals should focus on improving every touchpoint of the employee journey, from onboarding to career development and off-boarding.
Personalized employee experiences can make a significant difference. Tailor development plans, benefits packages, and recognition efforts to individual preferences and needs.
18. Measuring Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) HR Effectiveness
To gauge the effectiveness of HR strategies, establish key performance indicators (KPIs). These metrics can include turnover rates, employee satisfaction scores, time-to-fill job openings, and more. Regularly analyze these KPIs to assess the impact of HR initiatives.
Feedback loops are essential for HR effectiveness. Gather feedback from employees and managers to identify areas for improvement and refine HR practices continuously.
FAQ
1) What is the agile leadership model in HR?
The Agile Leadership model in HR emphasizes adaptability, customer-centricity, and cross-functional collaboration. It encourages an iterative approach, continuous learning, and empowerment of HR teams. Data-driven decision-making, experimentation, and efficiency are key, focusing on feedback, servant leadership, and delivering value to the organization.
2) What are the emerging opportunities for HR professionals in the future?
The future of HR holds exciting opportunities for those who can effectively address challenges and adapt to evolving trends. HR professionals will continue to play a vital role in shaping the success of organizations in the modern business landscape.
3) How will human resources operations adapt and adjust to future changes?
To adapt to future changes, human resources operations should embrace digital transformation, support remote and hybrid work, prioritize skills development and diversity, focus on employee well-being, leverage data and analytics, and adopt agile practices.
Compliance, remote onboarding, feedback mechanisms, leadership development, value-driven HR, flexible policies, global expansion, and sustainability efforts are also crucial for staying relevant and effective in a rapidly evolving work landscape.
4) How can HR professionals measure the impact of their work?
HR professionals can measure the impact of their work by utilizing various methods and key performance indicators (KPIs). These include gathering employee feedback through surveys, tracking turnover rates, assessing recruitment metrics, evaluating performance appraisals, and monitoring training and development outcomes.
Additionally, HR can measure cost savings, diversity and inclusion metrics, employee engagement levels, and compliance with labor laws. The use of HR analytics tools, market benchmarking, and feedback from leadership further contributes to assessing HR initiatives and demonstrating their value to the organization.
5) Why is attracting and retaining talent important in human resource management?
Attracting and retaining talent in HR management is paramount for organizations. It provides a competitive edge by fostering innovation, enhancing performance, and reducing turnover costs. Retained talent facilitates knowledge transfer, shapes organizational culture, and drives customer satisfaction. Moreover, it enables effective succession planning, adaptability to change, and developing a positive work environment.
A strong talent brand also aids in global expansion by attracting diverse local talent and building a favorable reputation. Talent acquisition and retention are ultimately integral to achieving business success and sustaining growth.
Conclusion
In the 21st Century, HRM faces many challenges, from technology integration to managing a diverse global workforce. HR professionals must be adaptable and continuously learn to navigate these challenges successfully. The future of HRM holds exciting opportunities for those who can effectively address these issues, as they play a vital role in shaping the success of organizations in the modern business landscape.
As we move forward, HRM will continue to evolve, and the HR professionals of tomorrow.
You Might Also Like
I am a Business and Management tutor passionate about Business, Management, Marketing, Operations Management, Finance, Economics, and HRM (Human Resource Management). Finished more than 1302+ online classes and exams for students. I ensure high scores while reducing their anxiety!"
Discount
On Your First Order




